Thoracic spine osteochondrosis (TOP) is a degenerative dystrophic (destructive) change in the functioning and condition of intervertebral fibrocartilaginous formations (disks).
This disease, despite its high prevalence, is characterized by the difficulty of detection in the initial stage of development, since its symptoms are similar to gastrointestinal diseases (peptic ulcer, gastritis, gastrologic syndrome in colitis), angina pectoris and, at times, times, myocardial infarction.

Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is very difficult to diagnose.
Less commonly, this disease is "disguised" as renal colic with cholecystitis or appendicitis. That's why you need to know the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine to correctly diagnose it and start treatment on time.
How does GOP osteochondrosis develop?
In the human spine (more precisely, in the spine) there are 33 to 35 vertebrae, which are connected by elastic discs, made up of connective tissue and a nucleus.
So, with the development of the disease (about 12 vertebrae), the connective tissues around the intervertebral discs are first deformed, due to which their elasticity decreases.
As a result, discs lose their inherent strength and elasticity, which over time leads to one of two scenarios:
- cracking of the discs, as a result of the appearance of intervertebral hernias;
- spinal deformity + damage to individual vertebrae in the spine.
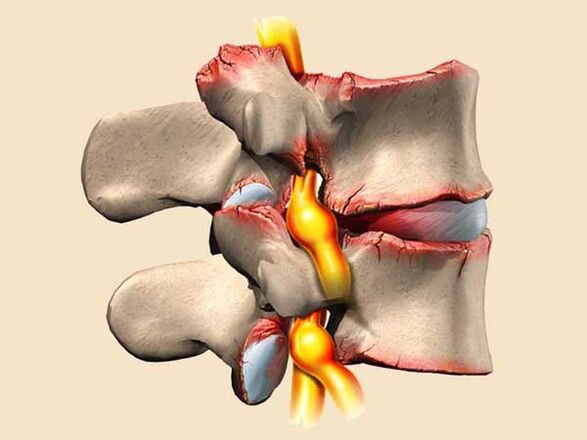
The second scenario is a consequence of the growth of bony bulges along the edges of the spine, their deformation and thinning.
There are 4 degrees of deformation in osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine:
- Reduced elasticity and height of the discs, bumps may appear.
- 2nd degree osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is characterized by a further decrease in the elasticity and height of the discs, instability of the GOP. As a result, the appearance of neurological symptoms or hernias.
- Formation of an intervertebral hernia.
- Discs lose shock absorbing properties. The vertebrae, approaching each other, almost completely lose their mobility.
Causes of disease
The main reason for the development of this disease is considered aging, because, according to statistics, the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region are usually found in people over 35 years old. This contributes to the deterioration of metabolism, the "accumulation" of injuries and the general wear and tear of the spine.
In other words, the older the patient, the more likely he is to detect signs of thoracic osteochondrosis.
But in fairness, it should be noted that recently, more and more patients between the ages of 19 and 30 are turning to neurologists with chest pains, which are increasingly being misdiagnosed as symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis. Doctors explain this dynamic with low physical fitness, poor nutrition, curvature of the spine and flat feet. These violations are typical of people who live in an urban environment with "office" work.

Common causes of development of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- spinal injury;
- genetic predisposition;
- immobility;
- overweight and smoking (metabolic disorders);
- prolonged exposure to the spine from incorrect postures;
- excessive loads;
- incorrect and poor nutrition (lack of fluid and trace elements);
- spinal overload due to various ailments or wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- stressful situations, nervous tension;
- violation of posture;
- diseases that lead to metabolic disorders.
Symptoms and signs of chondrosis of the chest
As already noted, the sensations in thoracic osteochondrosis (symptoms) often resemble other diseases as they are less pronounced compared to other types of this disease.
That is why it is very important not to engage in self-diagnosis, but to consult a qualified physician in case of prolonged, periodic, or "uncaused" pain in the thoracic spine.

Symptoms of GOP Osteochondrosis:
- pain between the shoulder blades when bending or lifting the arm(s) up;
- pain between the ribs when walking;
- with thoracic osteochondrosis, it is difficult to breathe with increasing pain during a deep inspiration or expiration;
- feeling as if back and chest were squeezed by an arc.
Chest pain in thoracic osteochondrosis appears:
- after or during a long stay in one position;
- slopes;
- physical activity;
- turns;
- at night.
Additional (special) symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, which may be masked as other diseases, especially in women:
- ringing and noise in the ears;
- frequent headaches;
- hoarseness and hoarseness;
- drops in blood pressure;
- limb numbness;
- burning sensation in the chest, similar to the sensations of pain in the heart in a heart attack, angina pectoris, or pathology of the mammary glands;
- in old age, frequent loss of consciousness;
- bouts of shortness of breath;
- constant tension of the neck muscles;
- frequent hiccups.

It is worth noting that in women, the symptoms of osteochondrosis of GOP are more pronounced, as their vertebrae are smaller and the connective tissue is thinner.
It is important to clarify that, contrary to popular belief, with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, body temperature does not increase precisely because of this disease. However, it can increase due to inflammatory processes caused by GOP osteochondrosis.
Pain characteristics
With osteochondrosis, pain in the sternum manifests as:
- Dorsalgia - mild, irritating, dull pain in the area of damaged discs, which gradually increases and lasts up to 2-3 weeks;
- Dorsago is a sharp, sharp, sharp pain during an attack of thoracic osteochondrosis, which is also called "chest back pain".
Diagnosis
Because osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is less common than other types of this disease, and its symptoms are typical of other diseases, establishing the correct diagnosis sometimes takes a lot of time (trial and error). And only after ruling out the most obvious options, doctors turn their attention to the symptoms of osteochondrosis.
Therefore, experts recommend contacting medical institutions specializing in problems with the musculoskeletal system in case of manifestation of characteristic pain sensations.
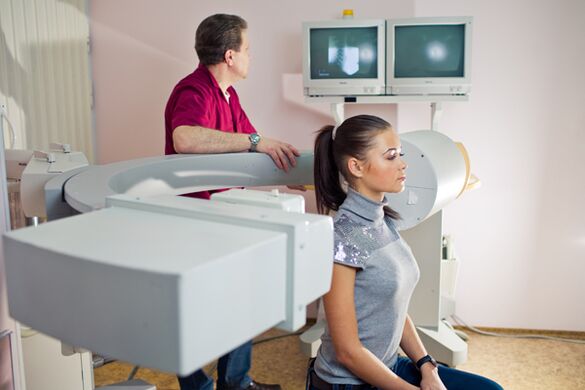
The diagnostic process itself takes place in 2 steps:
- Establishment of the primary diagnosis: examination and questioning of the patient. As a rule, this is done by a neurologist. Using a special technique, he examines the spine in various postures, states of rest and movement, paying attention to the body's structure, posture, and acute process line. After identifying signs of GOP osteochondrosis, a more detailed examination (finger) of the damaged area is performed to determine the location and degree of the disease.
- In addition, after the initial diagnosis, the patient is referred for a basic and more thorough examination of the thoracic spine: radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
How is GOP osteochondrosis treated?
Treatment is almost always carried out through conservative methods aimed at preventing the development of the disease, eliminating pain, and restoring spinal functions.
If that doesn't work, then surgery must be done.
Conservative treatment includes:
- physiotherapy;
- special diet;
- therapeutic block;
- massage;
- drug therapy;
- manual technique;
- spinal traction;
- reflexology;
- physical therapy exercises (LFK).
Prevention
The methods to prevent the occurrence of osteochondrosis GOP are very simple:
- prevent spinal hypothermia;
- avoid excessive loads;
- frequent change of posture during the "office", sedentary work and breaks every hour for 5-10 minutes;
- morning workout.



































